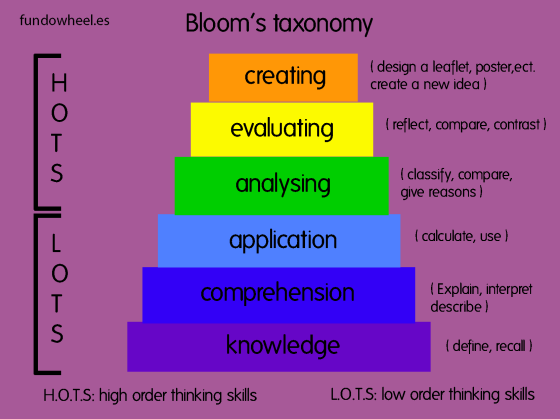
Benjamin Bloom (1956) divided learning into tasks or skills, which he called ”taxonomy». At the bottom the skills are relatively undemanding and they get more difficult, more connected and more useful towards the top.
He divided these six categories in «high order thinking skills» (H.O.T.S) and «low order thinking skills» (L.O.T.S). These skills are connected, only when you are completely proficient in one skill you can move to the next one.
- Low order thinking skills (L.O.T.S)
- Knowledge is the ability to recall something
- Comprehension means you understand the knowledge, you can explain in terms of your existing learning and experience
- Application means doing after being shown how
- High order thinking skills (H.O.T.S)
- Analysing is breaking a complex whole into parts, and then looking at the parts in some detail
- You can divide the whole into logical parts and then consider each part separately or;
- Looking at the whole, but only from a specific point of view
- Evaluating is making a judgement about an activity. Evaluation includes learners evaluating their own work while doing it, or after completing it
- Creating is using all the previous skills, the final process
- Analysing is breaking a complex whole into parts, and then looking at the parts in some detail
Debe estar conectado para enviar un comentario.